The influence of social relationships on a long life
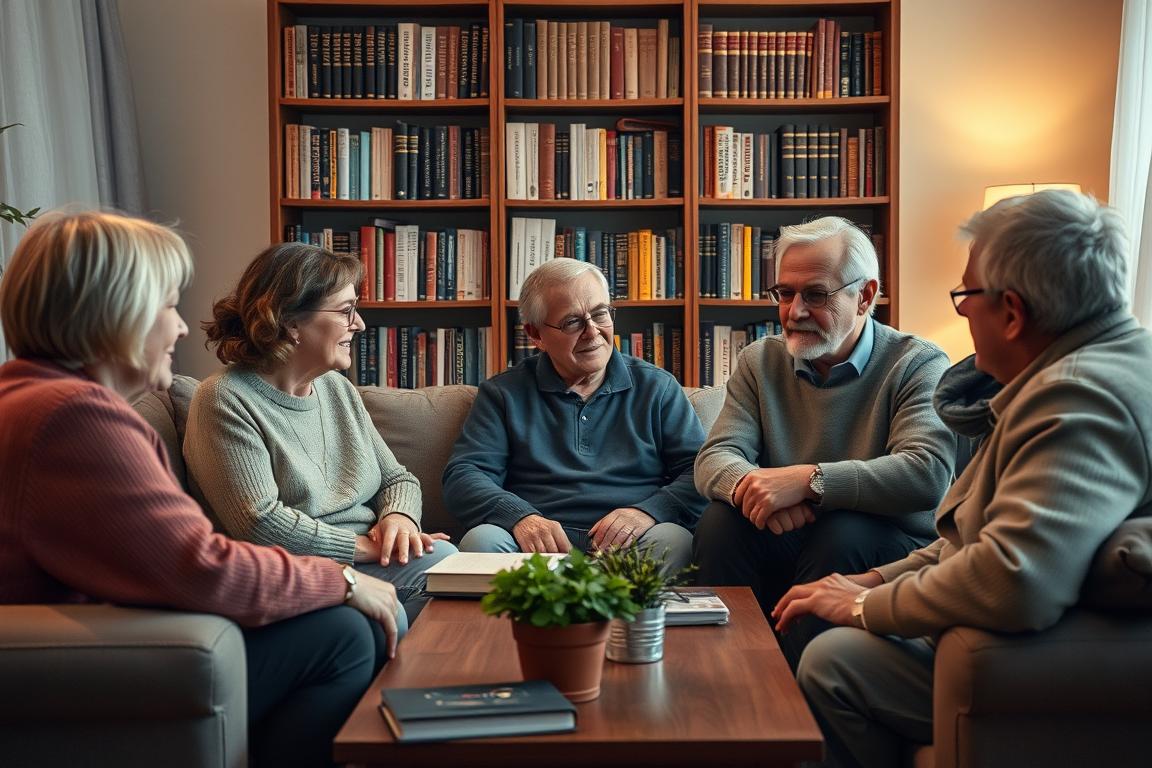
Did you know that older people with several good friends have a 22 percent higher life expectancy than those without a circle of friends? Social relationships are therefore not just a luxury, but essential for a long and fulfilling life. Studies show that close social networks are particularly strong in the so-called Blue Zones, such as Okinawa in Japan or Sardinia in Italy, and that these regions therefore have the highest life expectancy in the world.
However, the influence of social relationships goes far beyond the social network. They improve quality of life and promote both mental well-being and physical health. In fact, researchers at the University of Freiburg have discovered that just ten minutes with a best friend can provide an hour of stress relief.
Important findings:
- Older people with good friends have a 22 percent longer life expectancy.
- Close social networks in the Blue Zones contribute to a long service life.
- Ten minutes with a best friend can provide an hour of stress relief.
- Social relationships promote both mental and physical well-being.
- Social support improves quality of life and reduces the risk of death.
Why social relationships are important for health
Social relationships influence our mental health and physical health in many ways. Good friendships and close family ties provide emotional support and security, which reduces stress and promotes overall happiness. According to the Harvard study, which has been running since 1938, social relationships are more decisive for happiness than money, fame or professional success. Emotional bonds are therefore essential for a fulfilled life.
Psychological advantages
Close social ties offer protection against depression and anxiety. Lonely people release more of the stress hormone cortisol and have fewer immune cells compared to people with intact social relationships. A long-term study over more than 80 years shows that good relationships with others are crucial for a healthy life. Social interaction therefore not only promotes happiness, but also general mental health.
Physical advantages
On a physical level, social relationships promote activities that strengthen the cardiovascular system and encourage a balanced diet. People with close social ties are less likely to develop influenza, heart attacks and dementia. In addition, people who are socially isolated have higher levels of certain proteins in their blood that are linked to inflammation and diseases such as heart problems, diabetes and strokes. Social contacts therefore have a greater influence on health than fitness and diet.
Social contacts prolong life
Social contacts play a decisive role in extending life expectancy. Studies have shown that people with stable social ties have a significantly higher chance of living longer than those who are lonely or isolated. According to psychologist Ulrike Scheuermann, social contacts are the most important protective factor for health.
Chronic stress, which is exacerbated by a lack of social contact, damages almost all body and organ systems. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes stress as the greatest health risk of the 21st century. Social contact lowers stress levels and reduces the release of stress hormones.
In addition, social contact promotes the release of happiness hormones such as endorphins and the bonding hormone oxytocin. This leads to a sense of well-being and relaxation, which in turn can increase life expectancy. A 30-year study showed that strong relationships correlate with better health and longer life expectancy.
People with satisfying relationships also have a 50% higher chance of living longer than those who feel isolated. Good social contacts not only ensure emotional well-being, but also have a positive effect on physical health. Social isolation, on the other hand, increases the risk of heart disease, obesity and high blood pressure.
There is also no direct correlation between the number of social contacts and the feeling of loneliness. Introverts can be satisfied with few but deep connections. Stress at work contributes to people neglecting their friendships and becoming isolated. Conscious use of socializing time can be improved by reducing screen time.
The influence of social contacts is therefore unmistakable and essential for a long and healthy life. Social networks lead to less stress and depression and support the immune system and cardiovascular health.
Studies on the effects of social isolation
The social challenges associated with social isolation and loneliness are significant. Researchers and scientists worldwide are intensively investigating the impact of these phenomena on mortality risk. Social isolation and loneliness are independently associated with substantial health risks.
Increased mortality risk due to loneliness
One in five adults say they feel lonely, which can have a devastating impact on their health. Around one in four people experience some degree of social isolation. Prolonged loneliness is associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, cardiovascular disease and a weakened immune system. Studies have shown that people who feel lonely have a significantly higher risk of dying prematurely – up to 37% higher compared to people with adequate social relationships.
Independent effects of social isolation and loneliness
Social isolation can also have serious consequences independent of loneliness. People who are socially isolated have a 74% higher risk of death compared to socially active people. The differences in mortality rates between isolated and non-isolated individuals remain significant, even after accounting for other factors affecting health. Chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke and obesity are more common in socially isolated people. In addition, elevated levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, increase susceptibility to heart disease and other health problems.
The following table summarizes the key statistical results that illustrate the link between loneliness, social isolation and mortality risk.
| Factor | Increased risk (%) |
|---|---|
| Hardly any positive social contacts | 74% |
| Loneliness | 37% |
| Social isolation | 74% |
| Depression and anxiety | Long lasting |
| Heart attack or stroke | 30% |
In summary, both loneliness and social isolation can significantly increase the risk of mortality. To mitigate the negative effects of these two phenomena, it is important to take proactive measures and strengthen social networks.
Positive effects of friendships on life expectancy
Friendships play a crucial role in our lives and have a profound impact on our life expectancy. An Australian study shows that good friends can increase life expectancy, even more than family ties. This is because friendships are voluntary in nature and often provide a deeper emotional connection.
Stress reduction through social interactions
Stress reduction is one of the most important positive effects of friendships. Regular contact with friends can lower blood pressure and cortisol levels, as studies have shown. Support from friends during stressful times can reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems and help to reduce negative emotions.
Studies show that people who are accompanied by friends have a lower stress level, e.g. during exams. Research also documents that people with a close circle of friends have a 50 percent lower risk of dying, regardless of age, gender and social status.
Promotion of a healthy lifestyle
Friendships significantly promote a healthy lifestyle. Shared activities with friends, such as sports, increase physical activity and improve overall health. Germans do an average of 34 minutes of sport per day, and this figure increases through social motivation and engagement.
A healthy lifestyle, which is promoted through friendships, also includes a balanced diet. Cooking and eating together with friends often leads to better eating patterns and more mindfulness when dealing with food. Friendships also encourage positive behavioral changes that have been shown to increase lifespan by over 20 years.
Friendships are therefore not only a source of emotional support, but also an important factor for a healthy and longer lifestyle. Dr. Wolfgang Krüger recommends investing at least two hours a week in friendships in order to take full advantage of these positive effects.
Examples from the Blue Zones
The Blue Zones are regions of the world where people live significantly longer and healthier lives than the global average. These regions include Okinawa (Japan), Sardinia (Italy), Loma Linda (California), Nicoya (Costa Rica) and Ikaria (Greece). The inhabitants of these areas often live to a ripe old age, thanks to a lifestyle characterized by healthy eating, strong family ties and strong community life.
Community life and strong family ties
The community plays a central role in the Blue Zones. Regular social contact and close ties within the community promote not only physical but also mental well-being. In Okinawa, for example, people have a strong social network that gives them support and meaning in life. Studies have shown that people with a clear purpose in life can increase their life expectancy by up to seven years.
„The mountain villages of Sardinia are home to a particularly large number of men who reach the age of 100. The village community and the cohesion among family members contribute significantly to their long lives.“
Maintaining close personal relationships has a positive effect on health and reduces the risk of diseases such as dementia and heart disease. Community activities, such as attending church services together, can significantly extend life expectancy.
Healthy eating and social support
Another important aspect in the Blue Zones is a healthy diet. The inhabitants eat mainly plant-based foods, with meat only being consumed in very small quantities. In Okinawa, the 80 percent rule is common, where people stop eating when they feel 80 percent full. Studies show that the same eating style improves overall health and promotes longevity.
Fermentation is a common method of preserving food in these regions, which also contributes to better gut health. Plant-based foods, such as beans and whole grains, provide important nutrients and contribute to a healthy diet.
Support within the community also strengthens well-being. In the Blue Zones, the probability of reaching the age of one hundred is up to ten times higher than elsewhere. This proves that a combination of a healthy diet and social interaction contributes significantly to longevity.
Social support in old age
In old age, social support plays a crucial role in well-being and health. Recent studies, such as the meta-study by the Centre for Healthy Brain Aging (CHeBA), show that good social connections significantly reduce the risk of cognitive impairment, dementia and death. Importantly, these benefits occur regardless of the participants‘ country of residence.
An analysis of the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP) from 2021 found that 42% of people living in Germany felt lonely, compared to only around 14% in 2013 and 2017. This data underlines the increasing importance of support in old age. Frequent interactions with family and friends, whether monthly or weekly, can significantly reduce the risk of developing dementia.
Strong social networks can increase life expectancy by up to 50% and reduce the risk of death by at least 50%. Shared lifestyles and participation in community activities are particularly effective in reducing health risks. Studies show that lonely seniors have a higher risk of heart disease and stroke and that isolation increases the likelihood of death by 91%.
Marriage and close friendships also play a significant role. Marriage can reduce the risk of death by 15% for men and 8% for women. Close friendships and family relationships even reduce the risk of premature death by 45%. In addition, participation in religious and other group activities is associated with a 22% reduction in the probability of death.
The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the health risks of social isolation for older people, further emphasizing the importance of social networks. Regular social contact and participation in community activities are essential to maintain or improve well-being and quality of life in old age. It is therefore crucial that older people are well integrated into social networks in order to reap the many benefits.
The role of the family in social relationships
Family relationships are an essential part of our lives and play a crucial role in providing love, security and support. A strong family bond contributes significantly to health and well-being by providing both emotional and practical support.
Emotional and practical support
Emotional support from family is invaluable. Feeling loved and valued can reduce the risk of depression and promote overall mental balance. For older people in particular, this form of support contributes to greater life satisfaction and can slow down cognitive decline. Sociologist Nicolas Christakis emphasizes that close family relationships have a significant influence on health resilience.
On a practical level, the family can contribute to improving everyday life through various activities and services. Helping with household chores, caring for children or elderly family members and providing support in times of crisis are just a few examples. Statistics show that social contact, including strong family relationships, can extend life expectancy. Stable family relationships significantly improve recovery from illnesses such as strokes or heart attacks. Wilhelm and Jacob Grimm, the famous collectors of fairy tales, lived unusually long for their time, possibly due to strong family structures.
Tips for maintaining and expanding social networks
Expanding social networks and community engagement can make a significant contribution to improving quality of life. Active participation in social activities and a strong commitment to the community not only promote the maintenance of existing relationships, but also the development of new ones.
Active participation in social activities
The „Strengthening volunteering“ workshop on February 25, 2025 clearly demonstrated the importance of regular social interaction. Various social media channels, including those of the ASZ and the Kaiserslautern Yacht and Sailing Club, were discussed in order to increase reach and encourage participation. Daniel Helmes, Volunteer Coordinator, emphasized that many new channels often receive few or no comments, which requires gradual growth.
Involvement in the community
Strong community involvement was also observed during the 2023 mayoral election, which was accompanied by a volunteer team from the Open Channel. The „Engagierte Stadt“ organization of the ASZ celebrated its first birthday in February 2025, which was another milestone in the support and expansion of the social network. Such initiatives help to expand social networks and strengthen community involvement.
The regular office hours of volunteer coordinator Daniel Helmes, on Tuesdays from 4 to 6 p.m. and Thursdays from 9 to 11 a.m., are another example of how continuous support and involvement in the community can be cultivated. The next „Strengthening Volunteering“ workshop is scheduled for May 21, 2025 at 6:30 p.m. and offers another opportunity to actively participate and expand social networks.
| Event | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Workshop „Strengthening volunteering“ | February 25, 2025 | Discussion via social media channels |
| Mayoral election | 2023 | Deployment of volunteer teams |
| Committed city | February 2025 | First birthday |
| Next workshop „Strengthening volunteering“ | May 21, 2025 | Plans for participation and networking |
| Consultation hours Daniel Helmes | Always on Tuesdays and Thursdays | Individual advice and support |
Importance of social relationships for mental health
Social relationships play an essential role in mental health. They provide emotional support that can help prevent depression and boost self-esteem. People in stable partnerships or marriages generally live healthier lives than single people, which underlines how important social ties are for well-being.
Avoidance of depression and anxiety
The lack of social contact can have a significant impact on mental health. Lonely people are more likely to suffer from anxiety, sleep disorders and stress. Comparative studies show that people with good social networks are less likely to suffer from cardiovascular disease and have a higher level of life satisfaction. The prevention of depression and the general promotion of mental health are closely linked to the quality and quantity of social interactions.
„Social exclusion has similar negative health consequences as smoking or diabetes.“ – GEDA 2010
Strengthening self-esteem
A strong sense of self-worth is often the result of positive feedback and support from the social environment. Studies show that people who actively shape their social lives have a higher quality of life and are less likely to suffer from high blood pressure, obesity and other chronic illnesses. Social contacts can strengthen self-esteem as they convey a sense of belonging and appreciation.
| Effects of social relationships | Health benefits |
|---|---|
| Strong social networks | Fewer cardiovascular diseases |
| Emotional support | Greater life satisfaction |
| Active social life | Low blood pressure |
Joint activities and their health benefits
Shared activities are not only a wonderful way to deepen social connections, but also offer significant health benefits. Combining social encounters with active leisure activities such as sport or cooking together promotes both physical and mental health.
Sport and exercise in society
Sport and exercise in company are excellent ways to promote health and strengthen social ties at the same time. Studies show that people with a close circle of friends have a 50 percent lower risk of dying compared to loners. Joint sporting activities promote the release of happiness hormones such as dopamine and oxytocin, which can strengthen the immune system and reduce stress. Regular participation in sports groups or club activities not only increases physical fitness, but also supports mental health.
Cooking and eating together
Cooking and eating together can lead to a deep social bond and is associated with numerous health benefits. The structure, diversity and stability of social contacts have a positive influence on the risk of premature mortality. Studies show that shared meals and cooking groups improve mental well-being and reduce the risk of unhealthy eating habits in children and adolescents. Older people who are socially satisfied are around 40 percent more active than those who feel alone. When cooking and eating in company, not only is healthy food shared, but also stories and experiences, which in turn strengthens social and emotional bonds.
Social contacts and their role in dementia prevention
Regular social interaction plays a crucial role in preventing dementia. Studies show that social interaction and an active social life can significantly promote mental health.
Daily social interactions and mental health
Social interaction has positive effects on mental health as it helps to maintain cognitive functions. People who regularly participate in social activities have a 13% lower risk of dementia. Daily conversations and social engagements also help to stay mentally fit and reduce the risk of dementia.
Long-term studies and their findings
Long-term studies show that an active social life not only increases well-being, but can also counteract the progression of dementia. For example, social isolation in old age is associated with a 60 percent increased risk of dementia and explains 3.5 percent of all dementia cases. Another study of over 10,000 people with an average age of 73.8 years showed that physical activity can reduce the risk of dementia by 17% and social activity by 7%.
The research thus underlines the need for social interaction to prevent dementia and promote mental health at every stage of life.
Social ties for healthy ageing
Strong social ties are an important factor in healthy ageing, as they have a significant impact on well-being and quality of life in old age. The World Health Organization (WHO) has designated the decade 2020 to 2030 as the „Decade of Healthy Ageing“ to gather scientific evidence on how people around the world can age healthily. Close social networks provide emotional and practical support, which is essential for the well-being of older people.
In Germany, awareness of the importance of social ties in old age is steadily increasing. According to the Generali Ageing Study, just under one in 20 people over the age of 65 often feel lonely, which indicates strong family and social structures. Social interactions and regular interaction with family and friends promote mental fitness and contribute to the prevention of age-related diseases such as dementia. An English study shows that people with many social contacts at the age of 60 have a reduced risk of developing dementia.
In addition to social ties, regular physical activity also plays a key role. The WHO recommends that adults get at least 150 to 300 minutes of exercise per week. The Generali Ageing Study shows that the proportion of people over 65 who exercise regularly has risen from 1% in 1986 to 44%. Half an hour of moderate exercise a day can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of dementia by up to 60%. A combination of social contact and physical activity can therefore maintain a high quality of life in old age.