How long is conjunctivitis contagious for
Did you know that around 1.5 million people fall ill with conjunctivitis every year in Germany alone? What is particularly surprising is that the duration of infection varies greatly: While bacterial conjunctivitis is usually no longer contagious after 24 to 48 hours of antibiotic treatment, a viral form can remain contagious for several days to weeks. In this article, we take a detailed look at the different forms of conjunctivitis and explain how long which variants are contagious.
We also look at important measures to reduce the risk of infection, such as regular hand washing and avoiding hand-eye contact. Stay tuned to learn more about how you can protect yourself and your loved ones.
What is conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis, also known as conjunctivitis, is a common eye infection that is caused by various factors such as bacteria, viruses, allergens or environmental stimuli. This disease leads to unpleasant symptoms and discomfort that can severely affect the daily life of those affected.
Definition and causes
Conjunctivitis is defined by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin mucous membrane that covers the eye and eyelid. The most common causes of conjunctivitis are infections with bacteria or viruses, allergic reactions or irritative stimuli. Infectious conjunctivitis (bacterial or viral) is contagious, while allergic forms are not contagious. Some specific pathogens such as adenoviruses and herpes simplex viruses are particularly contagious, while less common causes such as chlamydia and gonococci can also lead to inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Symptoms and complaints
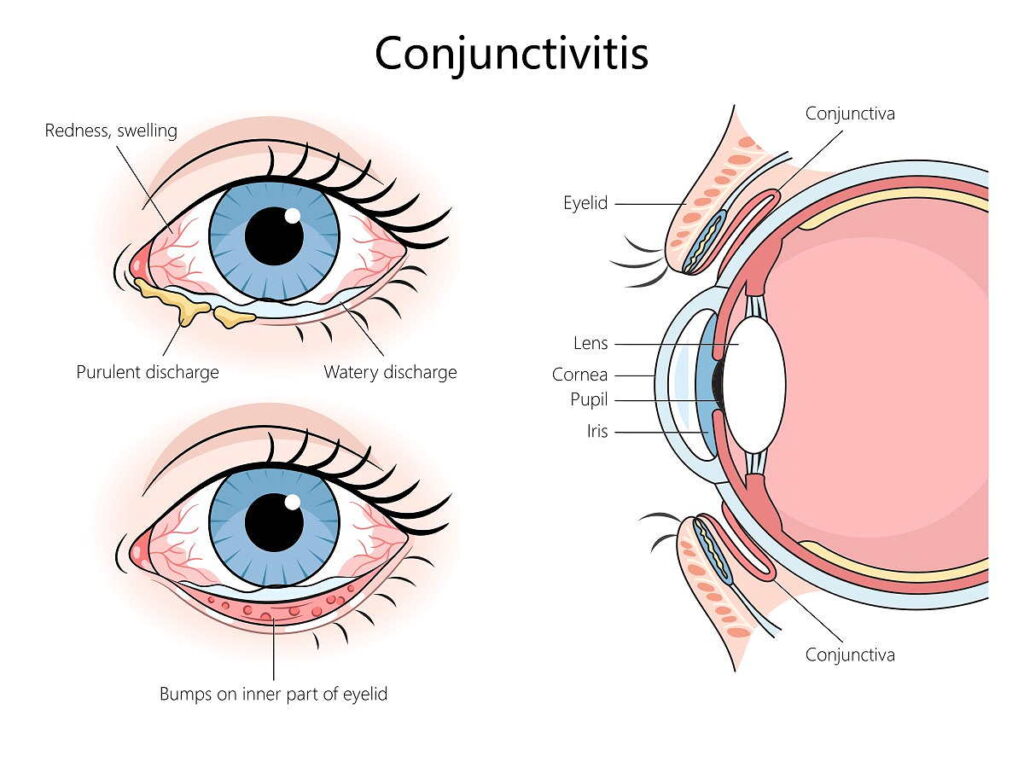
The symptoms of conjunctivitis vary depending on the cause. In general, they include redness, swelling, itching and increased tear production in the eyes. In the case of bacterial inflammation, there is often a secretion of white to yellow fluid, which leads to sticky eyelids. Viral conjunctivitis is characterized by a watery discharge, while allergic conjunctivitis often affects both eyes and is accompanied by allergic rhinitis.
Diagnosis by the ophthalmologist
An ophthalmologist is usually consulted to diagnose conjunctivitis. The doctor will carry out a visual examination of the eyes and may order laboratory tests to identify the exact pathogen. This procedure enables the cause to be determined and the best possible treatment to be initiated. In many cases, conjunctivitis heals within one to two weeks, but sometimes drug therapy is necessary, especially in the case of bacterial infections.
| Type of conjunctivitis | Symptoms | Healing time |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial | White to yellow fluid, sticky eyelids | 1-2 weeks |
| Viral | Aqueous secretion | 2-4 weeks |
| Allergic | Redness, itching, allergic rhinitis | Depending on exposure |
Different forms of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a widespread eye infection that can occur in various forms. Each type has its own specific causes, symptoms and treatment methods. A distinction is mainly made between bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis and irritant conjunctivitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci and other pathogens. This form of conjunctivitis is particularly contagious and can spread quickly through direct contact. Typical symptoms are a thick, white, yellow or green discharge from the eye. If left untreated, it usually heals within one to two weeks. A severe form of this disease, known as ophthalmia neonatorum, can occur in newborns within a month of birth and requires immediate medical attention to prevent serious eye damage.
Viral conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis is usually caused by adenoviruses and is also highly contagious. It can be transmitted through respiratory droplets or contact with contaminated objects. This form often starts in one eye and spreads to both eyes. Symptoms include watery secretions and severe irritation. Hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing the spread, especially regular hand washing and the use of separate towels.
Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is caused by allergens such as pollen, dust or animal hair and is not contagious. The main symptoms are white, viscous secretions and severe irritation of the eyes. This form often occurs seasonally and primarily requires avoidance of the triggers and symptom-relieving measures such as antihistamines.
Irritant conjunctivitis
Irritant conjunctivitis is triggered by external irritants such as chemicals, cigarette smoke or car exhaust fumes and is also not contagious. This form can also be caused by long-term use of eye drops containing preservatives, known as toxic conjunctivitis. Symptoms include redness and burning of the eyes. Treatment mainly consists of avoiding contact with the irritants and using protective eye drops.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: Highly contagious, causes purulent secretions.
- Viral conjunctivitis: Highly contagious, causes watery secretions.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Non-infectious, causes white, viscous secretions.
- Irritant conjunctivitis: Non-infectious, caused by external irritation.
How long is bacterial conjunctivitis contagious?
The duration of infection of bacterial conjunctivitis varies depending on the treatment and individual factors of the patient. Bacterial conjunctivitis can be contagious for several days to several weeks after symptoms appear. It is important that conjunctivitis is treated promptly to minimize the risk of infection.
Duration and course
As a rule, the symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis are no longer obvious after three to seven days, which means that the risk of infection decreases during this period. However, certain pathogens such as the adenovirus can remain infectious for weeks, especially if contaminated objects are not cleaned and disinfected.
Treatment and healing
Antibiotic treatment of conjunctivitis begins to take effect within up to 24 hours, which means that the conjunctivitis is no longer infectious. Complete healing can occur within a few days if the antibiotic therapy is carried out consistently. In the case of conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia, additional oral antibiotic therapy may be necessary to ensure a full recovery.
How long is viral conjunctivitis contagious?
The duration of infection of viral conjunctivitis can vary considerably, but typically it remains contagious for the entire duration of the symptoms. This can be a period of approximately 10 to 14 days. Symptoms often include redness, itching and increased tear production. The incubation period of viral conjunctivitis is approximately 1 to 12 days before the first symptoms appear.
Infection period
Viruses such as adenoviruses, which are often responsible for viral conjunctivitis, can survive on surfaces for up to 35 days. This makes adherence to rigorous hygiene measures crucial to prevent further spread. Patients should take particular care not to share towels, pillows and other personal items with others to avoid infection. There is often a risk of transmission for several days after the symptoms have subsided.
Soothing measures
There are no specific antiviral treatments for many viral eye infections. Therefore, soothing measures focus mainly on relieving symptoms. Affected people can use artificial tears to reduce dryness and apply cold compresses to relieve swelling and itching. Regular hand washing and the use of disposable wipes are also essential measures to reduce the risk of infection. Those affected should avoid contact lenses during the infection and minimize close contact with others during the first few days.
Measures to reduce the risk of infection
Strict adherence to hygiene measures is crucial to reducing the spread of conjunctivitis. Regular hand washing and disinfection are key components of these measures. This alone can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Hand hygiene and avoiding hand-eye contact
Hand washing is one of the most effective ways to reduce the transmission of germs. Frequent hand washing and proper hand hygiene help to reduce the number of germs on the fingers. In particular, direct contact between hands and eyes should be avoided to minimize the risk of infection.
Scientific studies have shown that the risk of spreading conjunctivitis can be significantly reduced by regularly disinfecting hands. This significantly reduces the number of infections.
Disinfection and cleaning of surfaces
In addition to hand hygiene, the disinfection of frequently touched surfaces plays an important role in preventing the spread of conjunctivitis. Regular cleaning and disinfection of door handles, light switches and other surfaces is essential. This successfully prevents the transmission of germs via indirect contact surfaces.
Avoiding close contact in communal facilities
In communal facilities such as schools, nurseries and hospitals, particular care should be taken to avoid close contact. Children with conjunctivitis should avoid such facilities as much as possible to avoid infecting others. Avoiding shaking hands and keeping a sufficient distance are effective measures to reduce the risk of infection.
| Furnishings | Measure |
|---|---|
| Schools | Hand hygiene, isolation in case of symptoms |
| Hospitals | Special hygiene measures |
| Kindergartens | Avoidance of contact, disinfection |
In the event of highly contagious infectious conjunctivitis, which must also be reported to the public health department, affected persons should be isolated and placed on sick leave. This is the only way to reduce the risk of infection and prevent the spread of the disease.
Treatment options for conjunctivitis
The treatment of conjunctivitis varies depending on the cause and type of inflammation. Drug treatments, home remedies and the importance of aftercare are explained below.
Drug treatment
Bacterial conjunctivitis usually heals within 7 to 10 days with the application of ointments or drops containing antibiotics. If the symptoms do not improve after 5 days, a new ophthalmologic examination is necessary. In the case of certain bacterial infections such as chlamydia or gonococci, antibiotics in tablet form may also be prescribed. It is also important to note that eye drops containing corticosteroids may only be used in very selected cases and after consultation with a doctor.
Home remedies and natural remedies
Home remedies such as cool compresses can help to alleviate the symptoms of conjunctivitis. In the case of viral conjunctivitis, which usually lasts 1 to 2 weeks without targeted antiviral medication, hygienic measures are particularly important, as you can still be contagious for several days after the symptoms have subsided. Allergic conjunctivitis can be treated with antihistamine eye drops prescribed by a doctor.
Importance of aftercare
Comprehensive aftercare is crucial to prevent relapses. This includes regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist and taking hygienic measures. In the case of chronic allergic conjunctivitis, desensitization (hyposensitization) can be considered. Increased protective measures should also be taken to prevent frequent conjunctivitis in the event of occupational exposure to irritants such as smoke or dust.
Preventive measures against conjunctivitis
The most important preventative measures against conjunctivitis include good eye care, protection from allergens and environmental factors and the safe use of contact lenses. Regular and thorough hand washing contributes significantly to preventing the spread of infections.
Correct eye care
Proper eye care is essential to prevent conjunctivitis. This includes cleaning your eyes daily with clean hands and suitable products. Sunglasses should be worn in strong sunlight to protect the eyes from UV rays.
Protection against allergens and environmental factors
Good allergen protection is important to avoid allergic reactions. This means that you should stay away from known allergens. This can include pollen, dust or animal hair. For people who are prone to allergies, special air filters in the home that remove allergens from the air can be helpful.
Safe use of contact lenses
The safe use of contact lenses plays a major role in the prevention of conjunctivitis. Contact lenses should always be inserted and removed with clean hands. Regular and careful cleaning of the lenses and their storage box can prevent infections. It is recommended that contact lenses should not be worn for longer than specified by the manufacturer.
When should you see a doctor?
A visit to the doctor is strongly recommended if symptoms of conjunctivitis do not subside within a few days, worsen or are accompanied by severe symptoms such as severe pain, visual disturbances or intense redness. Typical symptoms of conjunctivitis include red and swollen eyes, foreign body sensation, burning or itching, and increased tearing.
In the case of conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia or gonococci in particular, failure to treat can lead to a significant deterioration in vision and even blindness. Newborns are particularly at risk; an ophthalmologic examination and immediate treatment is necessary to prevent possible blindness. The rule of thumb for a visit to the doctor is: if the symptoms do not improve after two to three days, a specialist should be consulted.
A visit to the doctor is also important to ensure an accurate ophthalmologic examination and appropriate treatment. Conjunctivitis is highly contagious, which means that children with bacterial conjunctivitis should not be allowed to attend nursery in order to prevent the infection from spreading. Antibiotic eye drops can speed up the healing process of a bacterial infection and must be used exactly as prescribed. In the case of viral infections, antiseptic or moisturizing eye drops can provide relief.