Swollen eyelids: understanding symptoms and causes
Did you know that around 30% of the population struggle with puffy eyelids at least once a year? This unpleasant phenomenon can range from harmless consequences of lack of sleep to serious health problems.
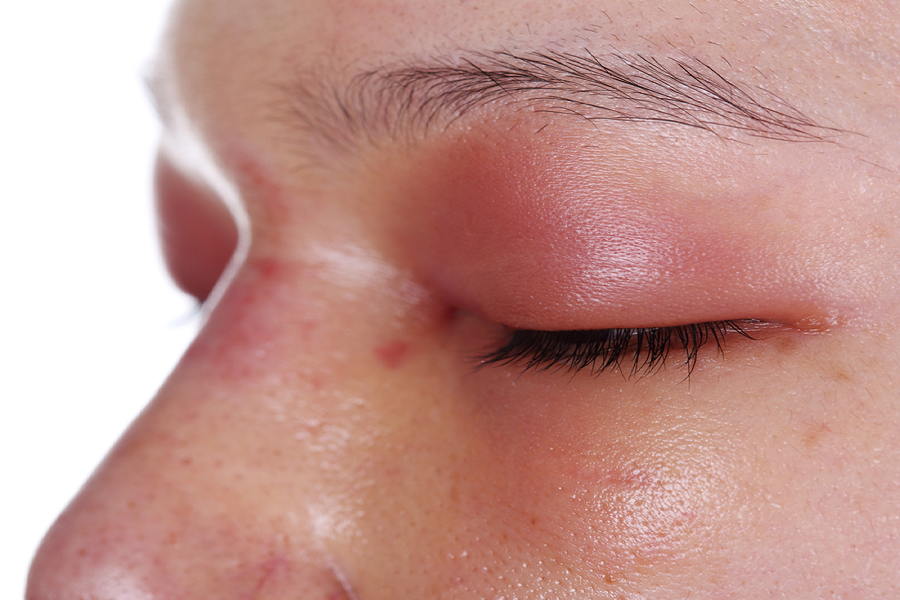
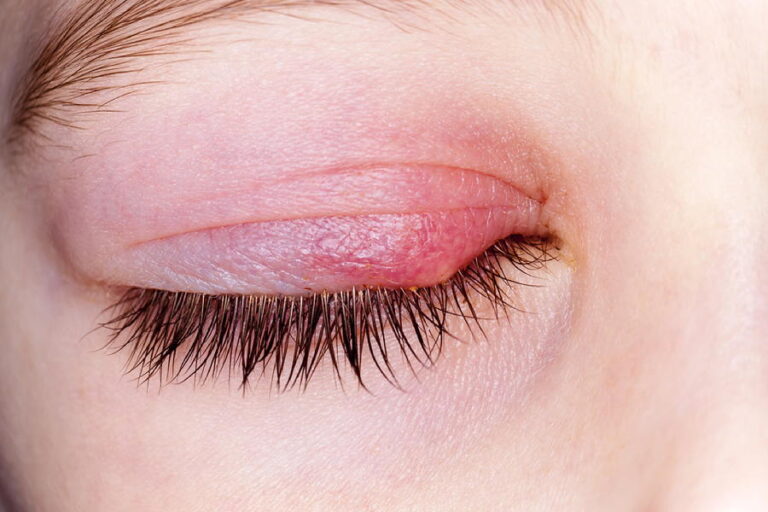
Swelling of the eyes is often caused by fluid retention or inflammation. Typical symptoms are reddened skin, itching or a feeling of tightness. Sometimes bags under the eyes also form or the eyelids feel heavy.
There are many triggers: allergies, infections such as conjunctivitis or even kidney problems. But everyday factors such as salty meals, stress or the wrong care products also play a role.
A doctor should always be consulted in the event of severe pain, visual disturbances or persistent symptoms. This article explains how you can identify causes, use targeted home remedies and take preventative measures.
The basics of swollen eyelids
We encounter numerous myths about swollen eyelids in everyday life – time for clarification. This area of the face reacts particularly sensitively to disturbances in the water balance and external influences.
Definition and delimitation
In medical terms, swelling of the eye refers to a visible enlargement of the eyelid area due to fluid retention. It is clearly different from “puffy” eyes, which usually occur temporarily after sleep.
| Feature | Swollen eyelids | Puffy eyes |
|---|---|---|
| Main cause | Inflammations, allergies | Lack of sleep |
| Type of liquid | Lymphatic fluid | Lacrimal fluid |
| Duration | Days to weeks | Hours |
Myths versus facts
A widespread misconception: salty foods always cause swelling. In fact, only one in three people are sensitive to it. Specialist studies show that environmental factors such as pollen or air conditioning often have a stronger effect.
Water plays a dual role – drinking too little can cause problems, as can excessive consumption before sleep. The balance of the body’s own fluid balance is crucial.
Identifying and correctly interpreting symptoms
Swollen eyelids often show characteristic features that indicate their cause. Precise observation helps to differentiate between temporary irritation and disorders that require treatment.
Typical signs of swelling
The following symptoms occur particularly frequently:
- Reddened or warm skin in the eyelid area
- Visible thickening with a feeling of tension
- Itching and increased tear formation
- Sticky eyelashes in the morning
| Symptom | Harmless cause | Warning signal |
|---|---|---|
| Slight redness | Short exposure to allergens | Purulent inflammation |
| Morning swelling | Sleeping position | Kidney problems |
When should medical advice be sought?
A visit to a specialist is recommended for these alarm signs:
- Sudden deterioration in vision
- Throbbing pain with fever
- Swelling that worsens over days
“Swelling with restricted movement of the eye always indicates serious causes – act immediately!”
Note changes to the skin and eyelid structure in the symptom diary. Photo documentation over 48 hours helps doctors with the diagnosis.
Causes of swollen eyelids: Allergies, infections and injuries
Many people know the problem: waking up with swollen eyelids for no apparent reason. There are often complex interactions between environmental influences and physical reactions behind this
Allergic reactions and environmental factors
Pollen, house dust mites or animal hair trigger histamine release in 20% of those affected. These lead to fluid retention in the eyelid area. Particularly insidious: contact allergies caused by make-up or care products that only react after hours.
| Allergen type | Duration of action | Typical symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Pollen | 15-30 minutes | Swelling on both sides |
| Cosmetics | 2-8 hours | Local redness |
Infections and mechanical influences
Bacterial inflammations such as styes are caused by blocked glands. Chalazion (chalazion), on the other hand, develops slowly due to chronic irritation. Mechanical causes often appear at night: sleeping on the side presses the face into the pillow, which impedes lymph drainage.
- Injuries due to eye rubbing
- Incorrect sleeping position (prone position)
- Unsuitable contact lenses
In many cases, simple tips help: Allergen avoidance, hypoallergenic cosmetics and increased sleep. If symptoms persist, an allergy test will clarify the triggers.
Practical tips for treating swollen eyelids
Effective treatment methods combine gentle techniques with targeted care. These strategies quickly alleviate discomfort and prevent renewed swelling.
Lymphatic drainage and care routine
Start in the morning with a 2-minute massage: circular movements with the ring finger from the root of the nose to the temples. Special creams such as Eucerin Hyaluron-Filler enhance the effect. Tip: Cooling gel sticks reduce bags under the eyes immediately.
| Care product | Effect | Application time |
|---|---|---|
| Hyaluronic acid serum | Moisturizing | In the morning |
| Caffeine roller | Decongestant | Acute case |
| Antihistamine gel | Allergy-inhibiting | Evening |
Cold applications and natural methods
Chilled metal spoons from the freezer work within minutes. Green tea compresses soothe allergic reactions. Important: Always consult a doctor first if you have a bacterial infection.
Testimonial from a user: “Since I have been using cucumber slices before going to bed, morning swelling rarely occurs any more.” Home remedies like this are the perfect complement to medical treatments.
Remember this rule of thumb: cold helps with acute allergic symptoms, heat with blocked glands. If in doubt, a skin test will clarify the causes of swollen eyelids.
Use of household remedies and everyday strategies
Natural methods often offer quick relief for puffy eyelids – if you use them correctly. Simple tricks from the kitchen and tried and tested routines can provide relief without expensive products.
Use of cucumber slices, tea bags and the spoon trick
Chilled cucumber slices have a cooling and decongestant effect due to their high water content. Place them on your closed eyes for 10-15 minutes. Green tea or camomile bags reduce inflammation thanks to their tannins. Tip: Store in the fridge for 10 minutes beforehand.
| Home remedy | Effect | Duration of application |
|---|---|---|
| Cucumber slices | Cooling, moisturizing | 10-15 minutes |
| Camomile bag | Anti-inflammatory | 15 minutes |
| Metal spoon (chilled) | Lymph flow stimulation | 5-8 minutes |
“Home remedies should never be used alone for bacterial infections – they can encourage the spread of the infection.”
Diet, fluid intake and sleeping habits
Low-salt food with potassium (bananas, spinach) regulates the water balance. Drink 1.5-2 liters of water throughout the day. Drink less liquid in the evening after 8 pm.
- Sleeping with your head elevated (2 pillows)
- Last meal 3 hours before going to bed
- Reduce alcohol and smoking
Be careful with self-diagnosed illnesses: Swelling caused by kidney problems or heart failure always requires medical treatment. A food diary helps to identify triggers.
Preventive measures and lifestyle changes
Healthy eyes start with conscious everyday decisions. Targeted adjustments can reduce puffiness in the long term and improve eye health.
Nutrition and fluid balance
A low-salt diet with potassium reduces water retention. Bananas, avocados or spinach are ideal. Drink 1.5-2 liters of water throughout the day – especially in the morning after getting up.
| Measure | Recommendation | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Dinner | Maximum 3g salt | Prevents nocturnal storage |
| Fluid intake | Last glass at 7 pm | Reduces bags under the eyes in the morning |
| Snacks | Almonds instead of potato chips | Provides vitamin E for skin elasticity |
Stress management and sleep optimization
Yoga or breathing exercises lower cortisol levels – a major cause of eye problems. Sleep with your upper body elevated (30 degrees) to promote lymphatic drainage.
“Doing 15 minutes of relaxation training every day not only improves the structure of your skin, but also prevents eye diseases.”
Fresh air and daily walks stimulate the metabolism. Combine these strategies with an evening skincare routine: apply cooling eye serum and massage with a jade roller.
Final tips for healthy eyes
Healthy eyes are a mirror of well-being. This sensitive organ requires conscious care and preventative measures. The combination of everyday strategies and medical knowledge provides long-term protection against complaints.
For people with sensitive eyes, a triad is worthwhile: root cause analysis, gentle treatments and regular check-ups. For this reason, you should keep a symptom diary in the event of recurring swelling. Another reason to take precautions: the tissue around the eyes regenerates more slowly than other areas of skin.
Proven home remedies such as cold compresses are an ideal addition to basic care. Antihistamines and special eye drops can help with allergy triggers. Third reason for mindfulness: unhealthy habits often only have a noticeable effect years later.
You support healthy tissue by:
- Salt-reduced diet with potassium sources
- Hypoallergenic care products without fragrances
- Regular breaks when working with a screen
People with risk factors should have an annual check-up. Make targeted use of home remedies, but seek medical advice if you are unsure. If allergies are suspected, special tests can clarify the triggers.
Your eyes deserve attention – start today with small changes. Every mindful approach pays off in clear vision and an improved quality of life.